Saxidomus gigantea Deshayes, 1839Common name(s): Butter clam, Washington clam, Smooth Washington clam, Money shell |
|
| Synonyms: Saxidomus giganteus |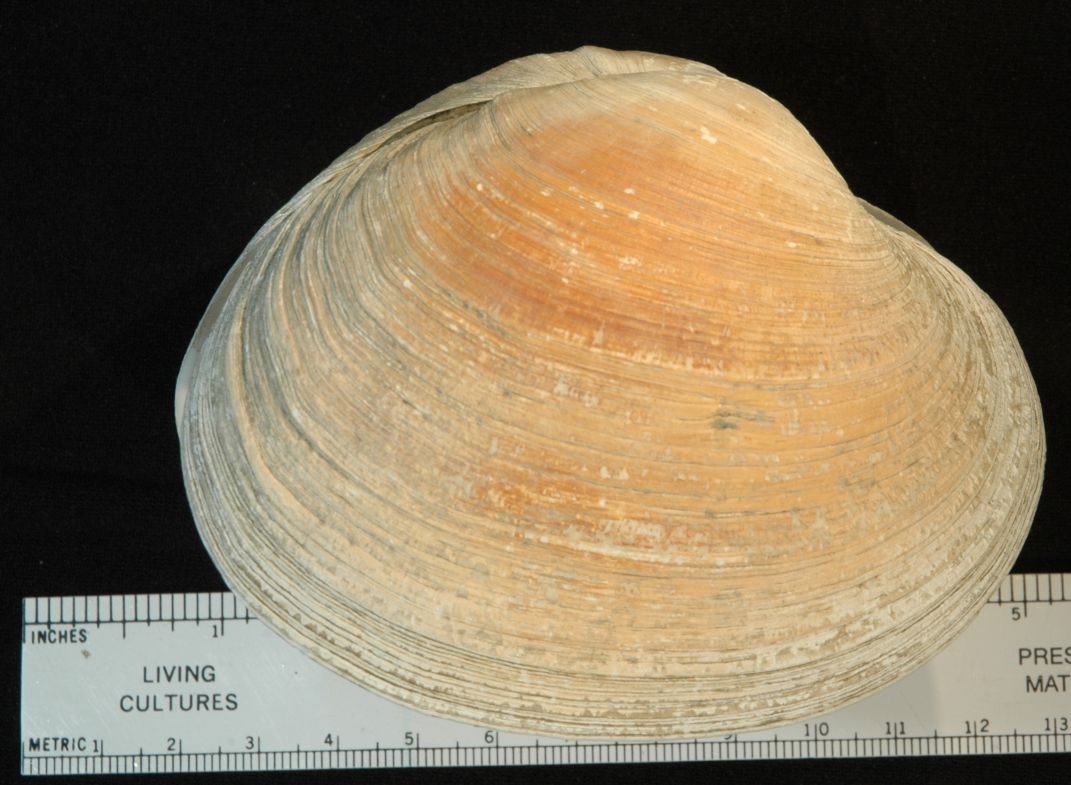  |
| Phylum Mollusca
Class Bivalvia Subclass Heterodonta Order Veneroida Family Veneridae |
|
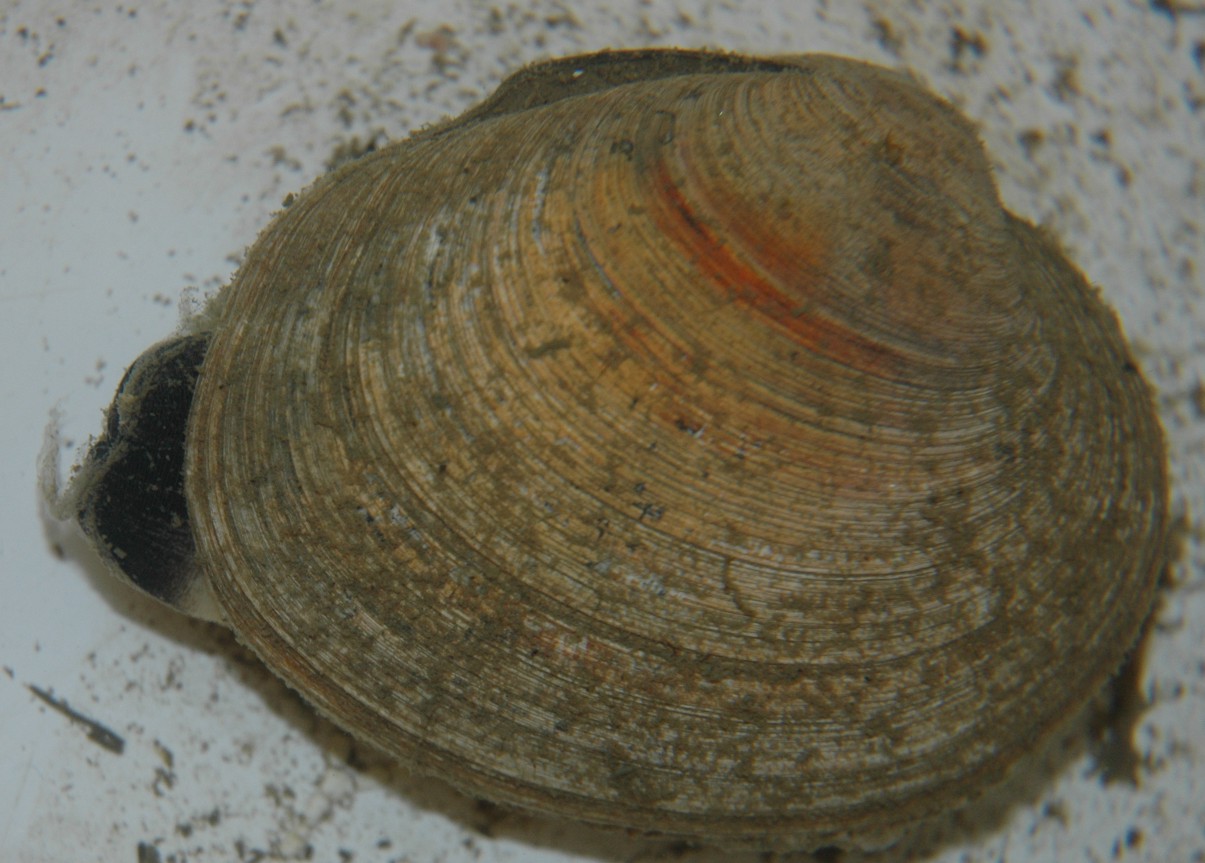
| Saxidomus gigantea shell from Padilla Bay, WA | |
| (Photo by: Dave Cowles, August 2005) | |
How to Distinguish from Similar Species: Of shells commonly found on the same, protected beaches, the cockle Clinocardium nuttallii has radial ribs and an undulating aperture where the two valves come together. The gaper clam Tresus capax and the softshell clam Mya arenaria have a large chondrophore at the hinge, and Tresus capax also has a large gape at the posterior end. The bentnose clam Macoma nasuta has valves bent to the right on the posterior end. The littleneck clam Protothaca staminea has fine radial ribs, a row of small teeth on the inside of the valves close to their ventral margins, and may also have a mottled pattern of periostracum. Saxidomus nuttalli is very similar but has more prominent raised concentric lines on the shell, plus the shell is stained purple inside. It lives primarily farther south in California.
Geographical Range: Aleutian Islands and SE Bering Sea, Alaska to San Francisco Bay, CA (rarely seen S of Humboldt Bay)
Depth Range: Low intertidal to 40 m
Habitat: Sheltered sand, sandy mud, and gravel beaches
Biology/Natural History: This species burrows moderately deep (to 35 cm), as suggested by the deep pallial sinus. It has been extensively commercially harvested, especially for clam chowder. Predators include the seastars Pycnopodia helianthoides and Evasterias troschelii, the moon snail Euspira lewisii, Dungeness crabs Metacarcinus magister, and sea otters. The species is especially vulnerable to carrying paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP), which accumulates especially in the dark tips of the siphons, so great caution should be used before eating them. The toxin, accumulated after the clam feeds on the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catanella, which blooms in sea temperatures over 13C, may persist for months in the tissues. Sea otters and seabirds seem to be able to detect the toxin and avoid tainted clams, though humans cannot. Pacific staghorn sculpins Leptocottus armatus nip off siphon tips, but after feeding on a tainted siphon will avoid them. Gulls regurgitate contaminated clams and avoid them after that. Pea crabs Pinnixa littoralis Pinnixa faba, or Fabia subquadrata may be found in the mantle cavity. The crystalline style contains many large spirochaete bacteria (Cristispira sp). Spawns in the summer. In British Columbia, about half the clams are large enough to spawn by their third year. Larvae settle from the plankton after 4 weeks. This species may live 20 years or more.
Indians formerly used the shells of this clam for money.
| Return to: | |||
| Main Page | Alphabetic Index | Systematic Index | Glossary |
References:
Dichotomous Keys:Fitch 1953
Flora and Fairbanks, 1966 (as Saxidomus giganteus)
Kozloff 1987, 1996 (as Saxidomus giganteus)
Smith and Carlton, 1975 (as Saxidomus giganteus)
General References:
Carefoot,
1977
Harbo,
1997
Harbo,
1999
Johnson
and Snook, 1955
Kozloff,
1993
Morris
et al., 1980
Niesen,
1997
Ricketts
et al., 1985
Sept,
1999
Scientific
Articles:
Moore,
Stephanie
K., Nathan J. Mantua, Barbara M. Hickey, and Vera L. Trainer, 2010.
The relative influences of El Nino-Southern Oscillation and Pacific
Decadal
Oscillation on paralytic shellfish toxin accumulation in Pacific
Northwest
shellfish. Limnology and Oceanography 55:6 pp. 2262-2274.
Web sites:
Washington
Dept of Fish and Wildlife clam page
General Notes and Observations: Locations, abundances, unusual behaviors:
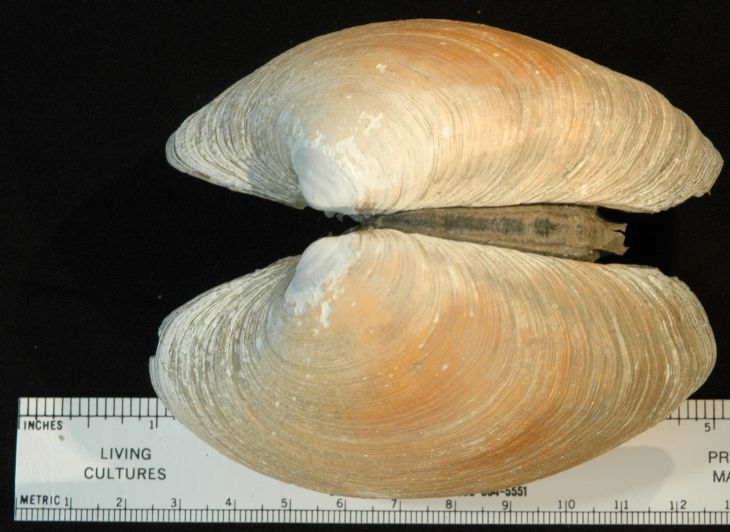

The hinge
ligament on Saxidomus gigantea is
external.
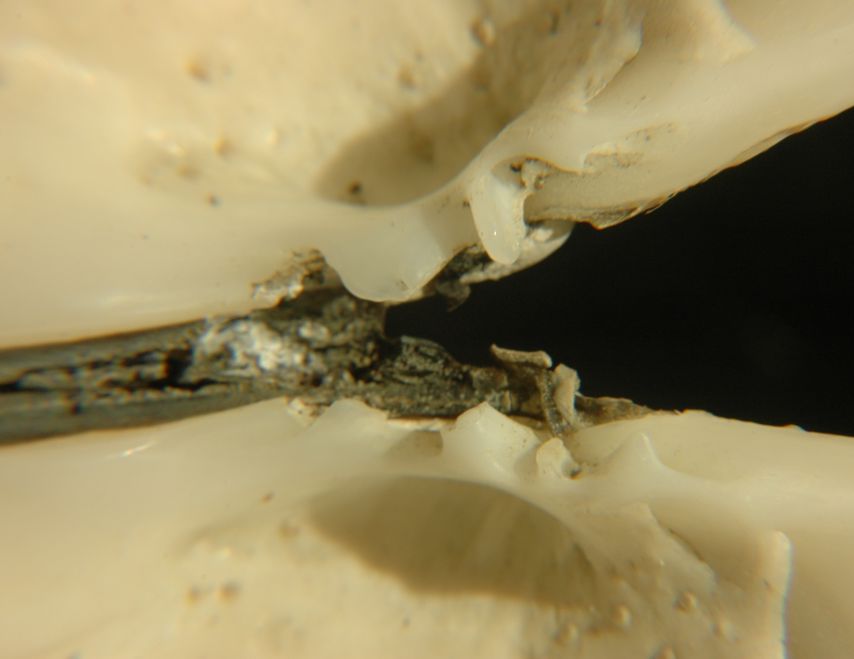
Saxidomus gigantea has three cardinal
hinge teeth on each valve
but no chondrophore.
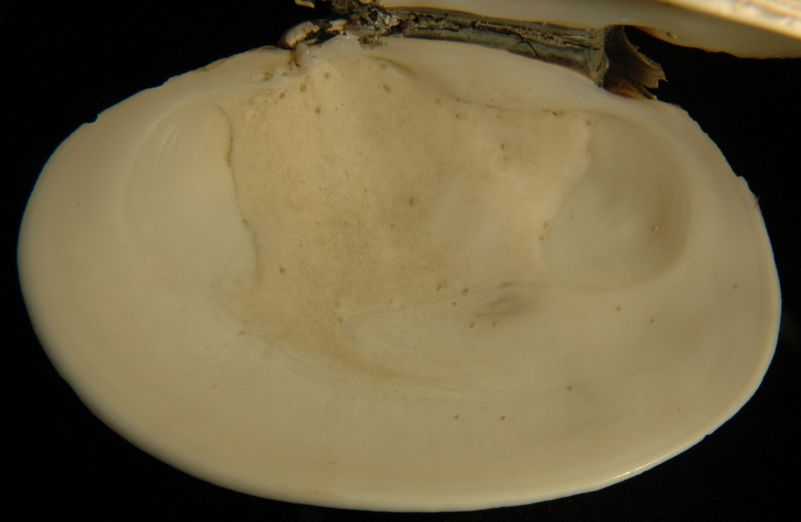

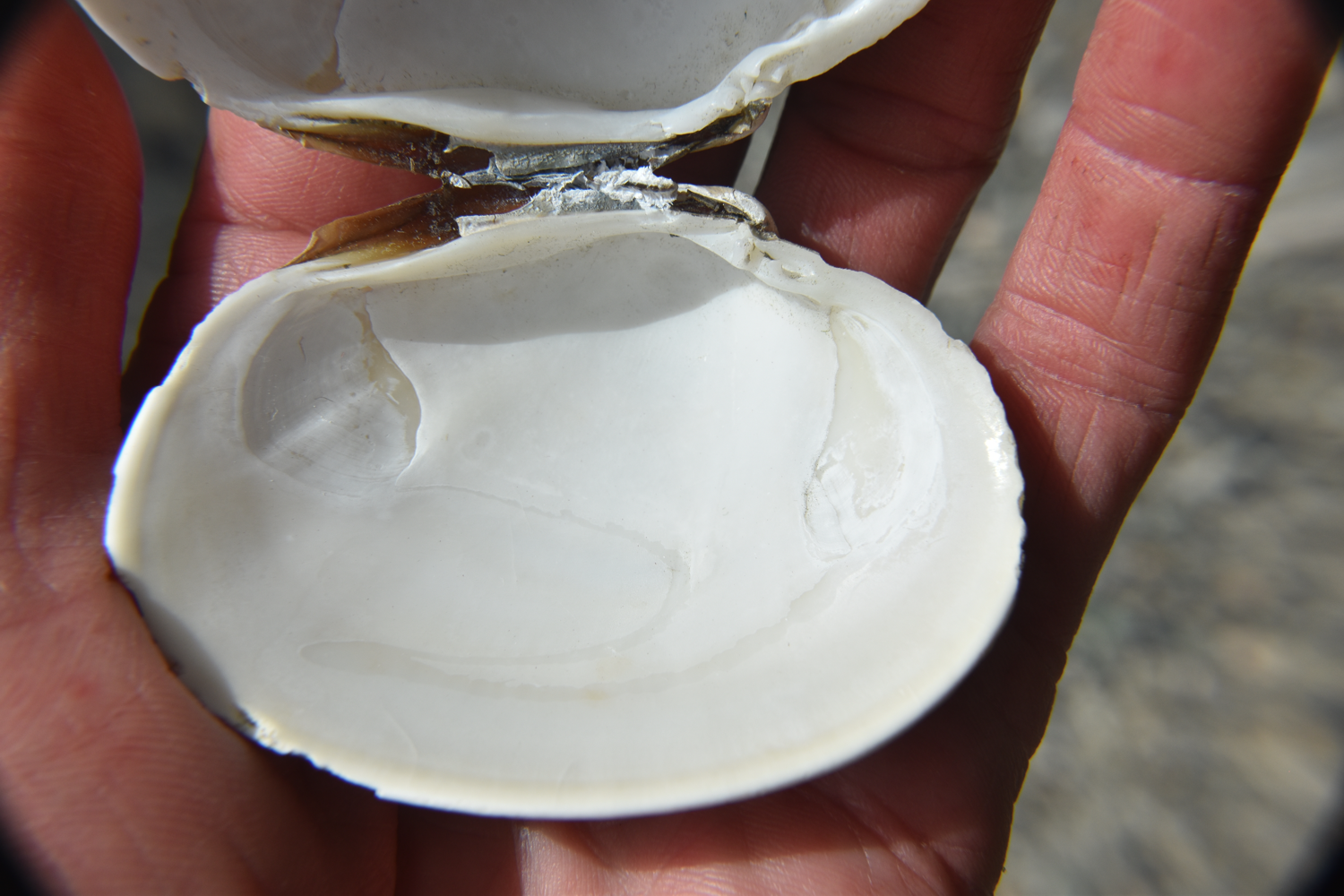
The two adductor
muscle scars are of similar size. There is a
continuous pallial
line and a well-developed pallial
sinus. This is the right valve.
The above photo, of the left valve, also shows the two distinct adductor muscle scars and the the pallial line with its deep pallial sinus.

The siphons
are united (attachedd to one another) and black on the tips.
Authors and Editors of Page:
Dave Cowles (2005): Created original page
