Psolus chitonoidesArmored Sea Cucumber, Creeping pedal sea cucumber, slipper sea cucumber |
|
| Synonyms: Psolus californicus | 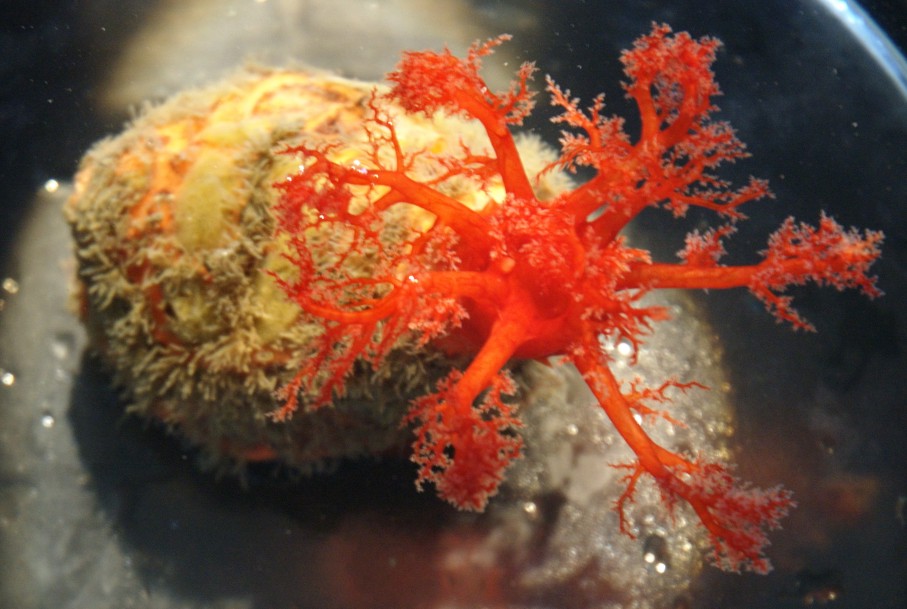 |
| Phylum Echinodermata
Class Holothuroidea Order Dendrochirotida Family Psolidae |
|
| Psolus chitonoides, about 6 cm long, found subtidally at Sares Head, WA. | |
| Photo by: Dave Cowles, July 2011 | |
How to Distinguish from Similar Species: Psolidium bidiscum is more purplish in color and is smaller (only up to 3cm long).
Geographical Range: Pribilof Islands and Gulf of Alaska to Baja California
Depth Range: Low intertidal zone to subtidal depths of 247m
Habitat: Rocks in exposed and sheltered inlets.
Biology/Natural
History: P. chitonoides
is essentially sedentary. The cucumber uses its ten equal tentacles
to filter detritus from the water. Sticky pads on each
tentacle capture
the food particles. The tentacles contain toxic compounds
called
saponins to discourage fish from nibbling at them. Predators
that
ignore these chemicals or are not affected by them include Stimpson’s
Sun Star, the Northern Sun Star, the Leather
Star, the Sunflower
Star, and the Red
Rock Crab. The animals spawn in the spring and a
large female
may release up to 34,700 eggs. The eggs form a lecithotrophic
larvae
followed by a pentacula
larvae. The larvae frequently settle in groups, usually on or
near
an adult.
| Return to: | |||
| Main Page | Alphabetic Index | Systematic Index | Glossary |
References:
Dichotomous Keys:
Carlton, 2007
Flora and Fairbanks, 1966
Kozloff, 1987
Smith and Carlton, 1975
General References:
Harbo,
1999
Kozloff,
1993.
Lamb
and Hanby, 2005
O’Clair
and O’Clair, 1998.
Ricketts
et al., 1985
Sept,
1999.
Scientific Articles:
Emlet, Richard B., 1994. Body forms and patterns of ciliation in nonfeeding larvae of echinoderms: functional solutions to swimming in the plankton? American Zoologist 34: pp. 570-585
Fankboner, P.V., 1978. Suspension-feeding mechanisms of the armoured sea cucumber Psolus chitonoides Clark. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 31: 11-25
McEdward, Larry R. and Benjamin G. Miner, 2006. Estimation and interpretation of egg provisioning in marine invertebrates. Integrative and Comparative Biology 46:3 pp 224-232
Young, C.M. and F-S Chia, 1982. Factors controlling spatial distribution of the sea cucumber Psolus chitonoides: Settling and post-settling behavior. Marine Biology 69: 195-205
General Notes and Observations: Locations, abundances, unusual behaviors, etc.:
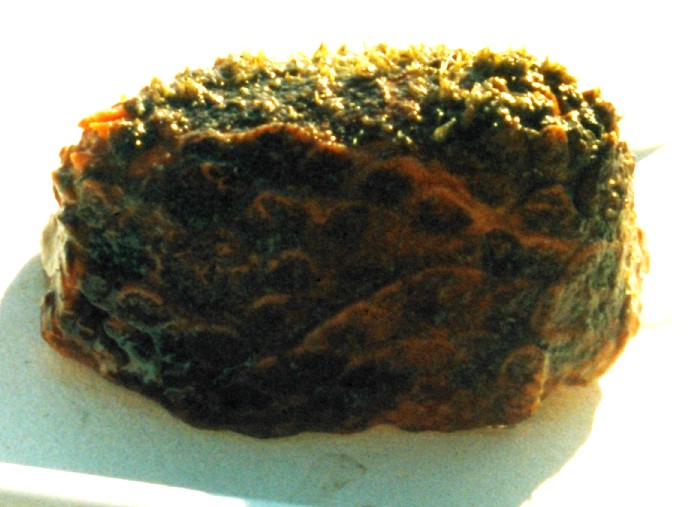

Another photo of Psolus chitonoides.
Noted the scalelike
plates the upper surface is covered in. The buccal tentacles
retract
into the opening on the top right.
Photo by Dave Cowles, August 1997. Total length about 5 cm.
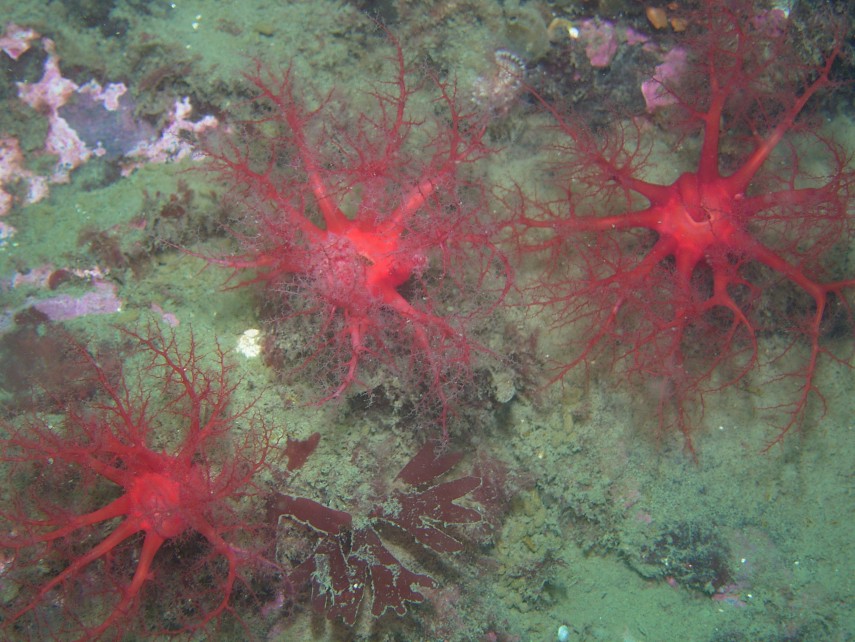

This species has bright red oral tentacles, as seen in this underwater
photo. Note the animal on the right has a tentacle in the
mouth to
remove adhered material.
Photo by Jim Nestler, July 2005
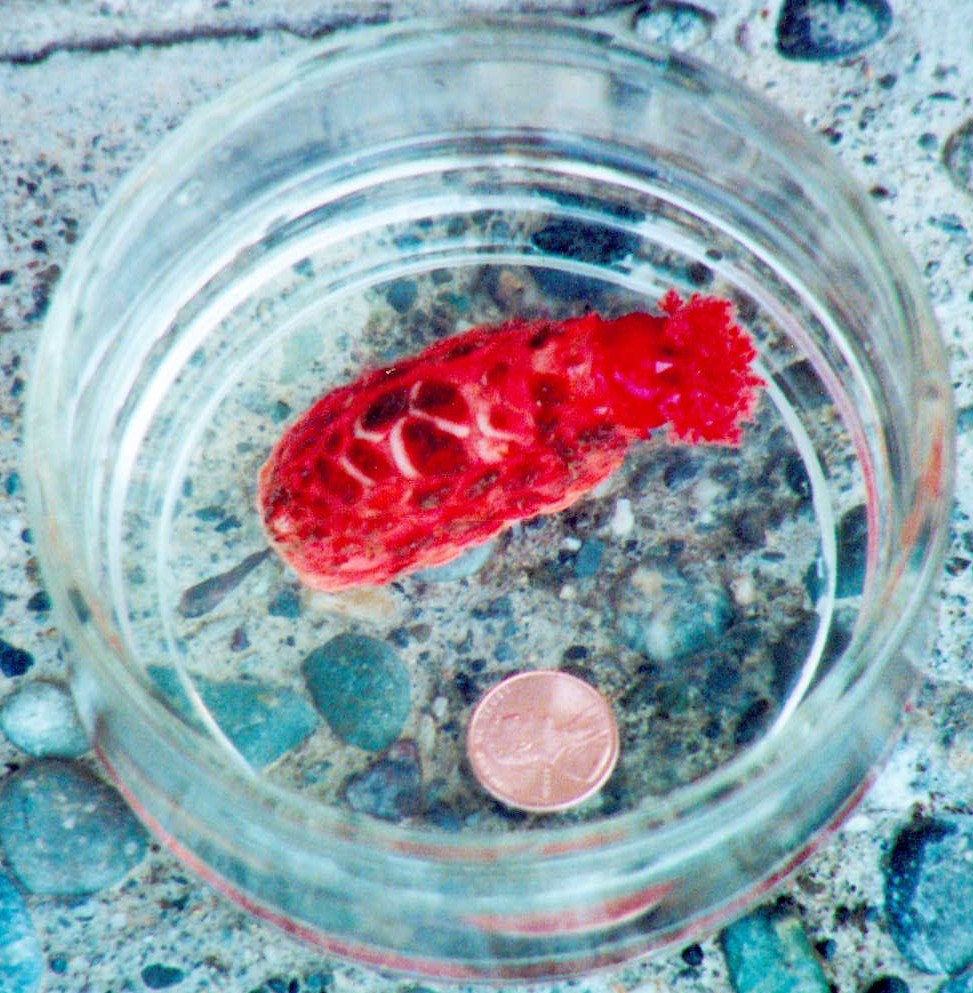

This 4 cm individual was photographed by Kelly Williams in 2002
Authors and Editors of Page:
Kelly Williams (2002): Created original page
Edited by Hans Helmstetler 12-2002, Dave Cowles 2005