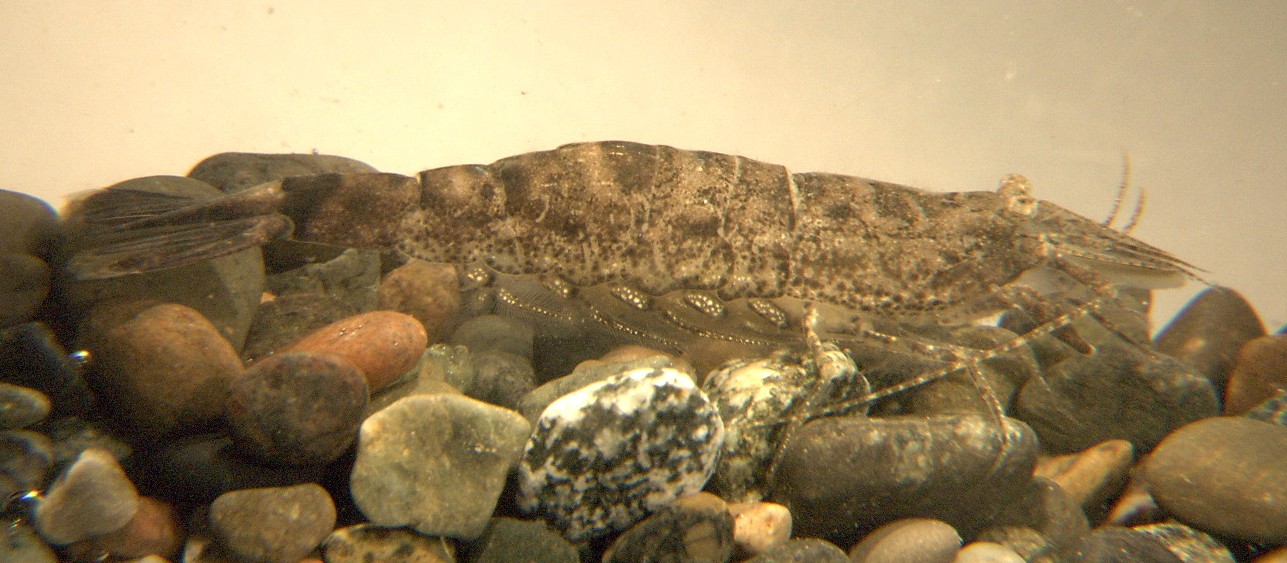
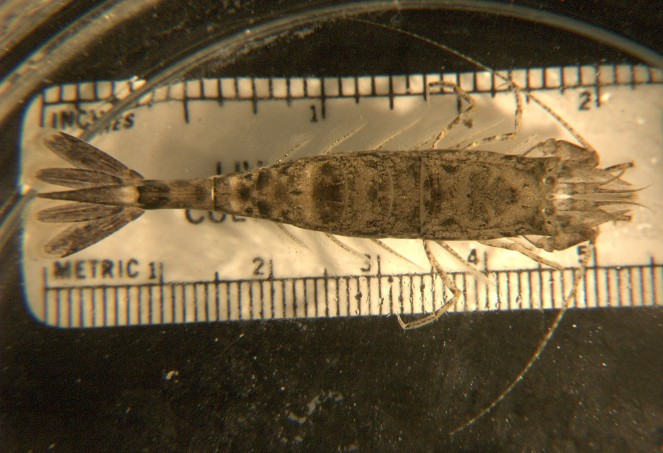
How to Distinguish from Similar Species: Crangon franciscorum has a spine on the upper posterolateral margin of abdominal segment 5. C. handi, C. alaskensis, and C. nigricauda have a median ventral groove on abdominal segment 6.
Geographical Range: East Pacific
Depth Range:
Habitat:
Biology/Natural
History: Crangon
shrimp are common on sandy bottoms, where their camouflage helps them
blend
in well. If disturbed they will often swim down to the sand,
rest
their ventral surface on it, and quickly burrow out of sight (using their legs, but probably
also using their pleopods--see the photo
below and this movie).
| Return to: | |||
| Main Page | Alphabetic Index | Systematic Index | Glossary |
References:
Dichotomous Keys:Kozloff 1987, 1996
General References:
Scientific Articles:
Campos,
Joana, Claudia Moreira, Fabiana Freitas, and Henk W. van der Veer, 2012.
Short review of the eco-geography of Crangon.
Journal of Crustacean Biology 32:2 pp 159-169
Web sites:
General Notes and
Observations: Locations,
abundances, unusual behaviors:
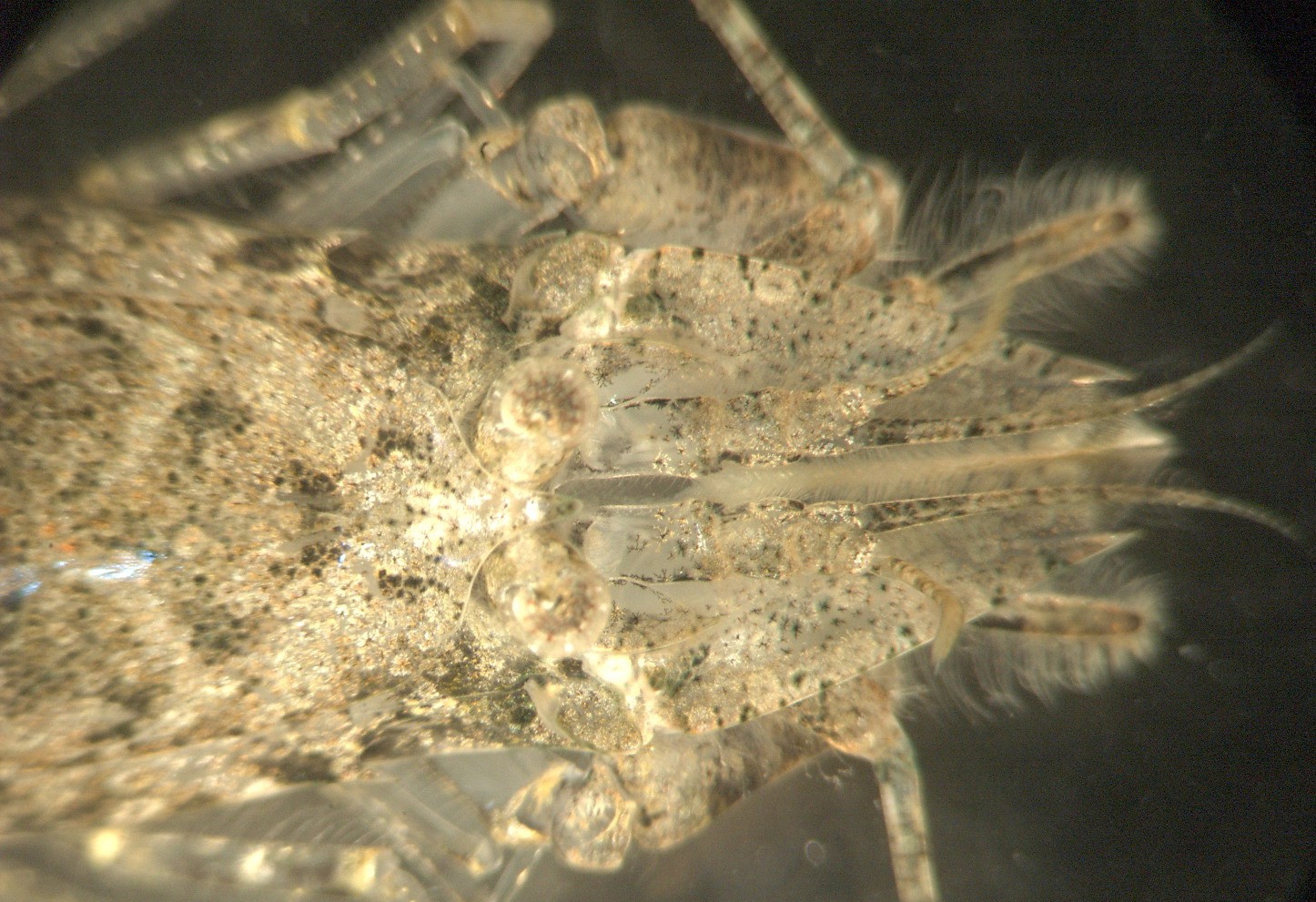
In this
underside (ventral) view of the
head the subchelate
first pereopods
can be clearly seen.

In this dorsal view of the head the small rostrum and the single median spine behind it can be seen. The arrangement of the eyestalks can also be clearly seen.
The
upper posterolateral margin
of abdominal segment 5 has no spines, as seen in this dorsal
view.
Anterior is to the right, and segment 6 is to the left.
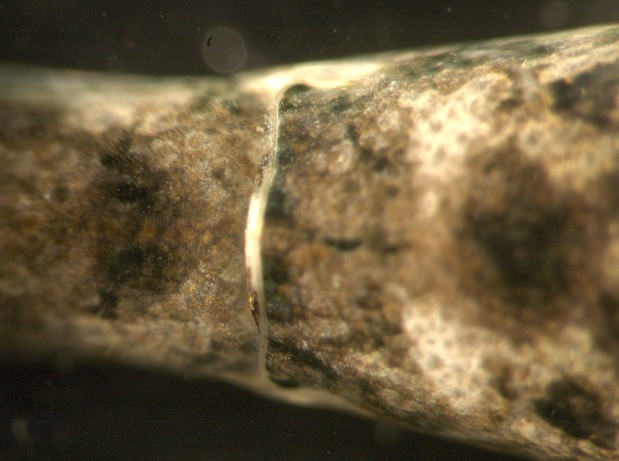

Abdominal
segment 6 has a dorsal
median
groove (sulcus)
but no median
ridge. Anterior is to the right and the tailfan is to the
left.
The
ventral sides of abdominal
segments 5 (right) and 6 (left) are both smooth and clear, with no median
groove (sulcus).
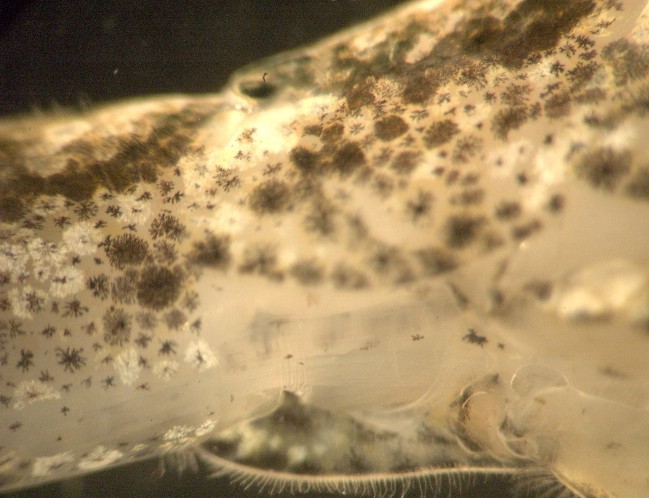
This view is an oblique view of the right pleura
and the ventral side from the right side of the shrimp. The
base
of leg 5 can be seen at the right.
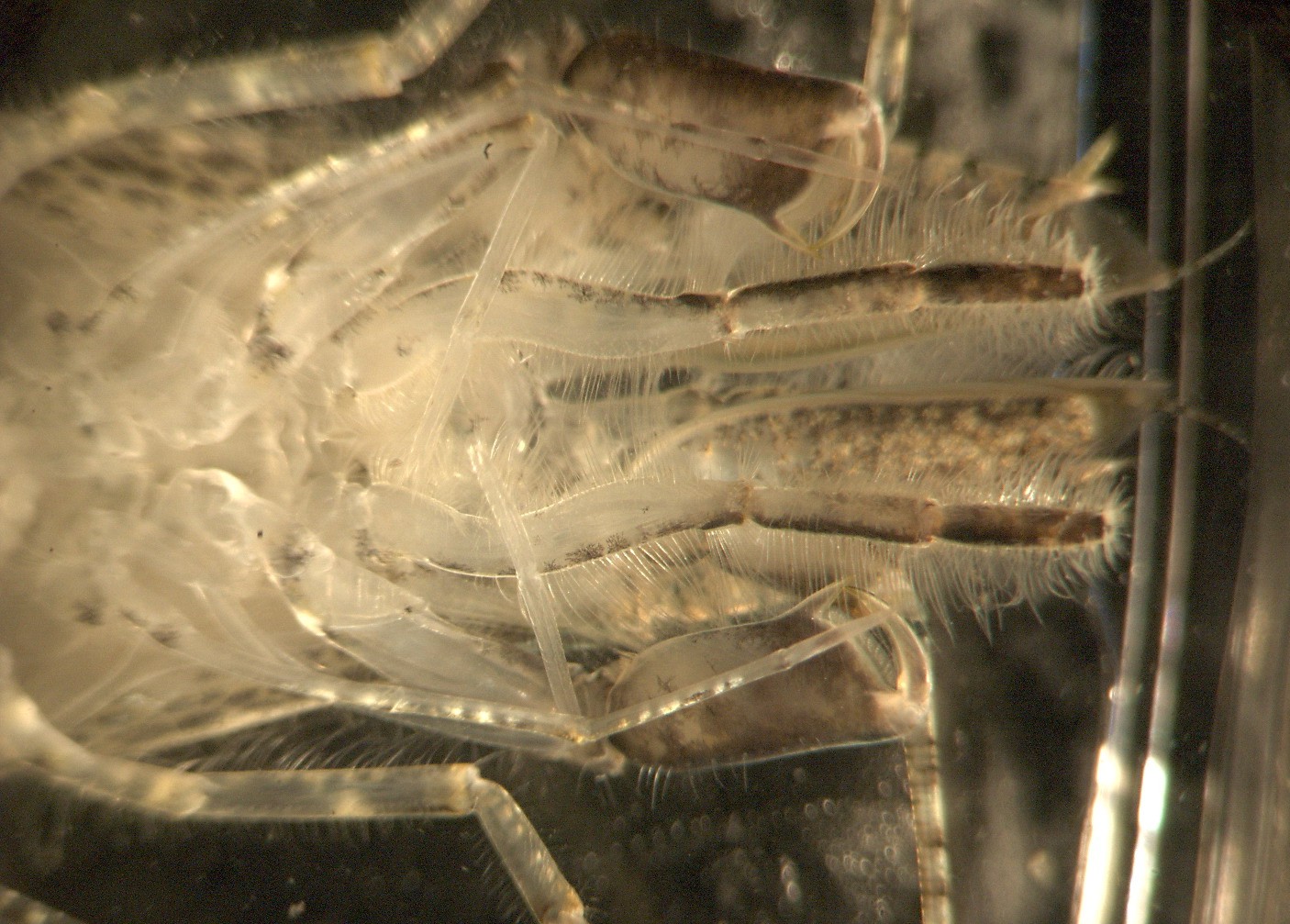
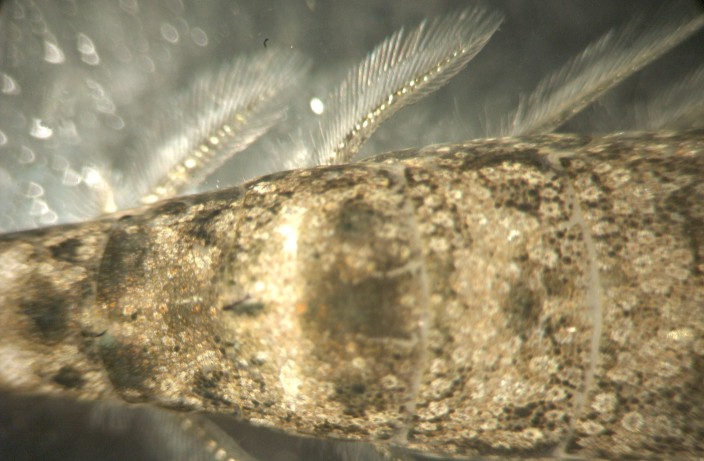
The feathery exopods
of the pleopods
are typically held out to the side. They are used for
swimming and
likely also for burrowing.

This individual
was
carrying a large batch of white
eggs.
Authors and Editors of Page:
Dave Cowles (2008): Created original page
CSS coding for page developed by Jonathan Cowles (2007)


